Space is becoming increasingly crowded, the high number of satellite launches have brought about a pressing concern: traffic management.
In recent years, a plethora of satellites have been deployed for various reasons, including Earth monitoring and internet constellations. The swarm of satellites is particularly frightening, as they launch a dozen at once.
For instance, SpaceX’s Starlink has deployed as many as 10,000 satellites to provide internet services in recent years.
One major issue is the increased possibility of hazardous collisions in low Earth orbit, where most satellites are placed.
On the other hand, many defunct satellites have lost power or run out of fuel after working for several years. These junk satellites float aimlessly in the vacuum and can trigger orbital collisions.
The need for innovative solutions has never been more urgent.
But what if satellites could be equipped with laser-activated license plates? That’s what a new study has proposed to prevent satellite collisions.
“Here we present a cooperative method to identify satellites from the ground by means of laser techniques,” the authors mentioned in the study.
This laser-based method may work even when the satellites run out of fuel or power. As a result, orbital debris can be tracked more effectively, reducing the chance of collisions.
“Satellite identification and tracking is fundamental for decision making in space traffic management,” noted the research paper published in the journal Communications Engineering.
How the satellite license plate works
Like a vehicle number, the Satellite License Plate (SLP) system serves as a unique satellite identifier. The New Scientist reports the plate system uses small cubic mirrors with light filters. These filters uniquely reflect laser light, acting as a license plate.
At the core of the SLP concept are retroreflecting tags mounted on satellites. These tags are unique in that they are spectrally encoded, ?? which means they reflect light in precise spectral patterns that can be decoded to identify them.
A laser can be fired at the mirror tags using optical ground stations. The station will transmit laser beams to the target spacecraft at various wavelengths. The light reflected can reveal the identity of the satellite.
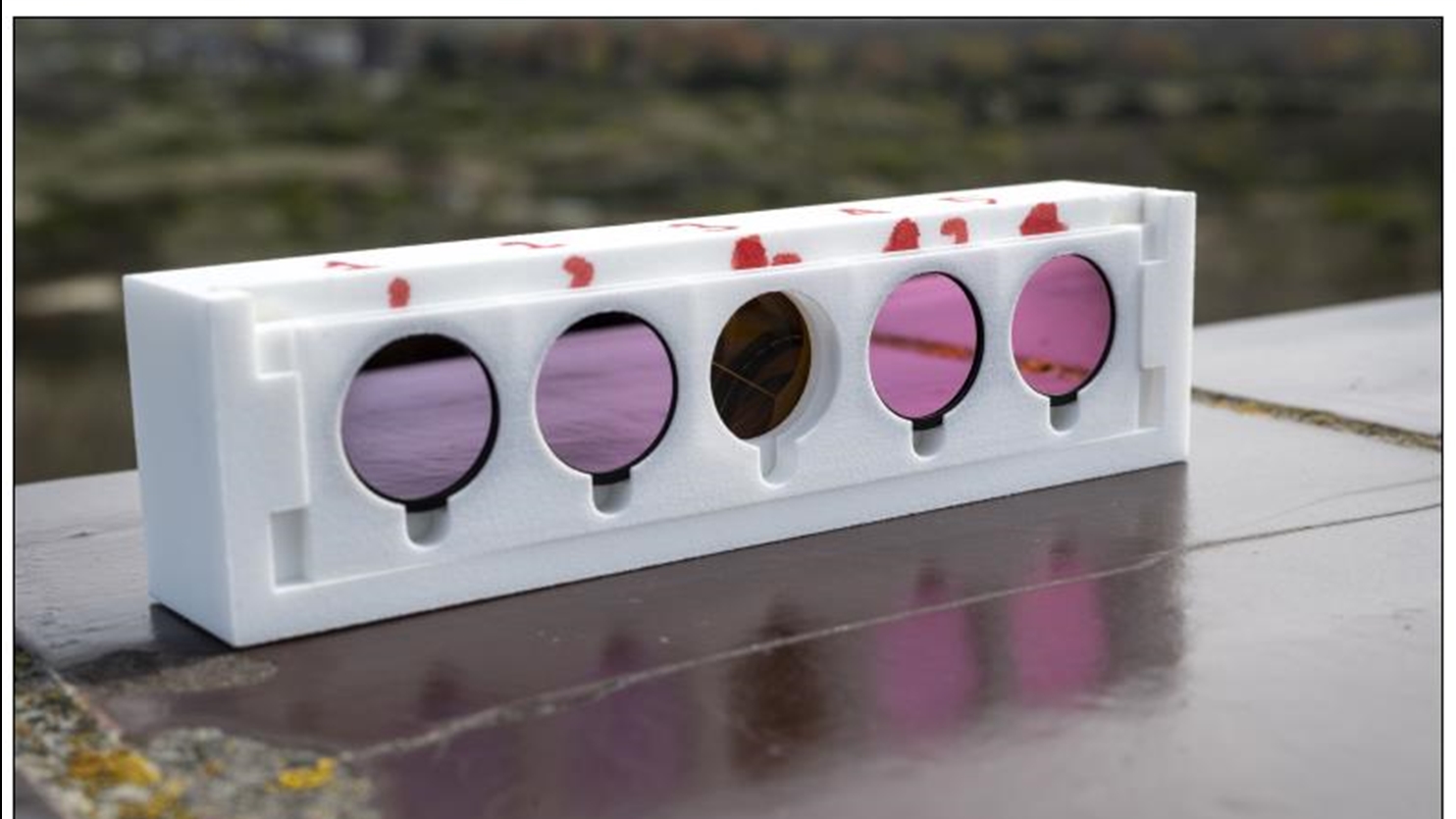

The method could work even on dead satellites
“We designed SLP so that the equipment can be installed in existing optical ground stations and make implementation swift and cost-effective,” said Fabrizio Silvestri, Optical System Engineer from the TNO High Tech Industry, in an earlier press release.
“In addition, the system can be used cooperatively between the satellite manufacturer and the launcher, to ensure clear identification of any unresponsive satellites after launch,” added Fabrizio, one of the authors of the new study.
One of the key advantages of the SLP method is its passive nature. This means the method does not require active participation from the satellites. Furthermore, its small design allows its installation on various satellite platforms without adding weight or complexity.
The technique may enable space agencies and organizations to detect and resolve dangerous collision scenarios in the near future.